Are you puzzled by the differences between a network switch and a router? Well, you’ve come to the right place! This blog dives into the fascinating networking world and explores the fundamental dissimilarities between these two essential devices. We’ll start by unraveling the basic definitions of a network switch and a router and then delve into their respective functionalities and importance. As we progress, we’ll uncover the disparities in their design and operation, shedding light on physical and internal component variations and operational disparities. But that’s not all – we’ll also compare their performance in terms of throughput, speed, latency, and packet loss and examine their scalability and flexibility features. Additionally, we’ll explore the different network topologies where switches and routers are utilized and delve into the crucial aspects of security and access control. To wrap it up, we’ll discuss the configuration and management procedures for these devices and the cost considerations and guidelines for choosing the right networking solution for your business. So, buckle up and get ready to embark on an exhilarating journey through
Understanding the Basics of Network Switch and Router
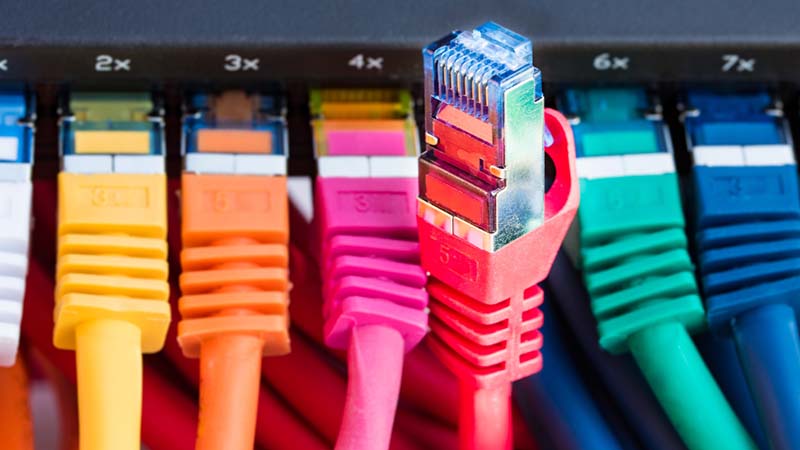
Let’s uncover the secrets of network switches and routers! These two crucial devices are fundamental in managing data traffic within a computer network. While a network switch acts as a bridge connecting multiple devices within the same local area network (LAN), allowing them to communicate, a router is responsible for directing data packets between different networks.
The functionality of both the network switch and router is nothing short of fascinating. The switch operates at layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model, making lightning-fast decisions based on MAC addresses to forward data frames to their intended destinations efficiently. On the other hand, routers work at layer 3 (Network Layer) by analyzing IP addresses to determine the most efficient path for data transmission between networks.
Understanding these basics about network switches and routers is essential because they are key components that enable seamless communication across modern computer networks. While switches are used internally within LANs to connect devices like computers, printers, and servers, routers serve as gateways between different networks such as connecting your home or office network to the internet. It’s truly remarkable how these devices make it possible for us to access information online from anywhere in the world!
Differences in Design and Operation
When it comes to physical design, network switches are usually designed with multiple Ethernet ports for connecting devices within a local area network (LAN). On the other hand, routers typically have fewer Ethernet ports as their main function is to connect different networks together, such as a LAN to a wide area network (WAN), using various interfaces like Ethernet or Wi-Fi. This means that switches are more focused on facilitating communication within a single network, while routers are geared towards interconnecting different networks.
Regarding internal components, switches primarily rely on MAC addresses to forward data packets to the appropriate devices within the same network. They operate at Layer 2 of the OSI model and make forwarding decisions based on MAC address tables. Routers, however, work at Layer 3 of the OSI model and utilize IP addresses to determine how and where data should be routed between different networks. This fundamental difference in addressing enables routers to intelligently route traffic across disparate networks based on destination IP addresses.
Operational variations between switches and routers stem from their respective design focuses. Switches excel at providing high-speed connectivity within a single network by efficiently directing data traffic directly from one device to another through MAC address learning processes without involving complex routing decisions. Conversely, routers focus heavily on interfacing with multiple networks by making intelligent routing decisions based on IP addresses and maintaining routing tables that dictate how data should flow between interconnected networks.
Comparison of Network Switch and Router Performance
Regarding throughput and speed, the network switch excels in handling high data transfer rates between devices within a local area network (LAN). With its dedicated connection for each device, the switch can maintain high speeds even when multiple devices communicate simultaneously. On the other hand, routers prioritize efficient routing of data packets between different networks or subnetworks. This means that while switches focus on internal communication speed, routers optimize external data transfer, making them essential for connecting to networks like the Internet.
Regarding latency and jitter, network switches and routers play crucial roles in maintaining smooth data transmission. Network switches reduce latency by minimizing the time data packets take to reach their destination within a LAN. This is especially beneficial for real-time video conferencing or online gaming applications. Routers also contribute to low-latency performance by efficiently forwarding packets across different networks with minimal delay. Additionally, they help manage jitter by ensuring consistent packet delivery times, vital for maintaining stable connections.
Furthermore, both network switches and routers have distinct functions when it comes to packet loss and error handling. Switches are designed to minimize packet loss within a LAN environment through efficient switching mechanisms that reduce collisions and improve overall reliability. In contrast, routers focus on error detection and correction when transferring data between different networks or subnets. They utilize protocols such as TCP/IP to ensure accurate information delivery while detecting potential errors.
Scalability and Flexibility of Network Switch vs Router
When it comes to scalability, network switches in uk offer an impressive level of expandability. With the ability to connect multiple devices and handle heavy traffic flow, switches are ideal for growing networks. Whether you need to add more computers, printers, or other devices, a switch can easily accommodate these additions without sacrificing performance.
On the other hand, routers also provide scalability but in a different way. Routers excel at managing different networks and directing traffic between them. This makes them essential for large-scale networks that require connectivity across various locations or departments. With advanced routing protocols and support for diverse network types, routers are designed to grow with your organization’s expanding networking needs.
In terms of flexibility, both network switches and routers offer unique advantages. Switches provide flexibility within local area networks (LANs) by enabling efficient data transmission between connected devices. Routers bring flexibility on a broader scale by facilitating communication between different networks while ensuring secure and optimized data transfer. Depending on your specific networking requirements, both devices offer valuable options for creating adaptable and reliable network configurations.
Understanding Network Switch and Router Topology
Trying to wrap your head around the difference between a network switch and a router? It’s like stepping into the exciting world of networking topology! When we talk about LAN topology, we’re diving into local area networks – think office or home setups. A network switch is like the conductor of this symphony, directing traffic within the local network at lightning speed. On the other hand, when we move onto WAN topology, it’s all about wide-area networks that connect devices across larger geographical areas. This is where routers come into play as they navigate and guide data packets through complex pathways to reach their destination.
What happens when you venture into hybrid topology? You’re getting a taste of both LAN and WAN configurations in one intricate setup. Things get exciting because switches and routers team up to create seamless communication across various locations. The switches ensure swift data transmission within each location while the routers manage the interconnections between these sites. It’s like watching a well-choreographed dance performance unfold before your eyes – every device has its role in ensuring smooth connectivity.
So dive into this captivating world of networking topology where switches and routers take center stage in creating efficient communication systems for businesses, homes, and everything in between!
Security and Access Control in Network Switch and Router
Regarding security features, network switches often focus on port-level security, using mechanisms such as MAC address filtering and VLAN segmentation. These features allow for granular control over which devices can communicate with each other within the local network, helping to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
On the other hand, routers are designed to provide higher-level security measures, such as firewall capabilities and VPN support. Routers inspect incoming and outgoing traffic at the network layer, making decisions based on source and destination ip addresses and port numbers. This allows for more comprehensive protection against external threats from the internet or other networks.
Both network switches and routers can implement Access Control Lists (ACLs) to define rules for permitting or denying traffic based on various criteria. However, while ACLs in switches typically focus on controlling traffic within the local network, router ACLs extend their reach to include traffic passing between different networks or subnets.
Network Switch and Router Configuration and Management
Configuring a network switch is an exhilarating experience as you dive into creating VLANs, setting up port security, and managing Quality of Service (QoS) policies. The process involves connecting to the switch via a console or SSH, then using a command line interface (CLI) or web-based user interface to customize settings according to your network requirements. It’s like being an architect designing the blueprint for a high-speed data highway!
On the other hand, configuring a router opens up doors to adventure as you establish dynamic routing protocols such as OSPF or EIGRP, implement Access Control Lists (ACLs), and configure Network Address Translation (NAT). You can navigate different routing tables and craft intricate route maps dictating how data packets travel through the network. It’s akin to being a trailblazer mapping out paths in uncharted territories!
Regarding management, both network switches and routers offer an array of tools such as SNMP for monitoring device performance, Syslog for tracking system events, and NetFlow for analyzing traffic patterns. Managing these devices is like having a control center where you can oversee data flow, troubleshoot any issues that arise, and ensure optimal network infrastructure functionality.
Cost Considerations for Network Switch and Router
Regarding the initial investment, network switches are usually more cost-effective than routers. Businesses can allocate their budgets more efficiently when considering their networking needs. With lower upfront costs, companies can invest in quality switches without breaking the bank.
Looking at the total cost of ownership (TCO), network switches continue to shine as a cost-effective option. Maintenance and operational expenses are generally lower for switches than routers, making them a wiser long-term investment. Businesses can benefit from reduced TCO by choosing network switches in UK over routers, allowing them to allocate resources towards other aspects of their operations.
Moreover, considering return on investment (ROI), businesses will find that network switches offer better value for money. Handling high data traffic volumes with minimal latency makes network changes a valuable asset in any organization’s infrastructure. This allows companies to optimize their networks and enhance productivity while maximizing ROI.
Choosing the Right Networking Solution for Your Business
When setting up your business network, choosing between a network switch and a router can be quite exciting! It’s like choosing the perfect tool for the job – you want to ensure you’re getting exactly what your business needs. By carefully assessing your business requirements and evaluating your network needs, you can make an informed decision that will set your business up for success.
The beauty of this process is that you can tailor your networking solution specifically to meet your unique business needs. Whether it’s high-speed data transfers or seamless communication across multiple devices, there’s a networking solution out there waiting for you. By understanding the differences between a network switch and a router, you’ll be well-equipped to find the perfect fit for your business.
So get ready to dive into the world of networking solutions with excitement! With careful consideration and expert advice, you can select the ideal option to keep your business running smoothly and efficiently.
“Networking Arts is a top business IT solution provider and UK IT hardware reseller, specializing in Cisco software license solutions and network switches. Our products include wifi modems, routers, wireless access points, computer accessories, and more. As IT equipment suppliers in the UK, we are committed to providing high-quality products and managed IT services to meet the diverse needs of our clients. Focusing on delivering reliable and efficient IT solutions, Networking Arts is the go-to source for all your business IT needs in London and beyond.”
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a network switch?
A network switch is a device that connects multiple devices within a local area network (LAN). It operates at the data link layer of the OSI model and uses MAC addresses to forward data packets to the intended destination device.
2. What is a router?
A router is a networking device that connects multiple networks, such as LANs and WANs. It operates at the network layer of the OSI model and uses IP addresses to route data packets between different networks.
3. What is the main difference between a network switch and a router?
The main difference between a network switch and a router is how they handle data packets. A switch forwards data packets within a LAN based on MAC addresses, while a router routes data packets between different networks based on IP addresses.
4. Can a network switch replace a router?
No, a network switch cannot replace a router. While a switch is used to connect devices within a LAN, a router is required to connect multiple networks and handle the routing of data packets between them.
5. Do I need a network switch and a router in my network?
In most cases, yes. A network switch connects devices within a LAN, while a router is necessary to connect multiple networks and provide access to the internet. However, a combination device called a router switch may fulfill both functions in small home networks.
network switches and routers, highlighting their differences in design, operation, performance, scalability, flexibility, topology, security, configuration, and cost considerations. It helps businesses understand the importance of choosing the right networking solution based on their needs and requirements.